50+ Top Video & Film Editing Terms (Beginner’s Glossary)
Video and film editing can be filled with technical jargon and terminology and it’s hard to keep track of what everything means, particularly if you’re just starting out. We’ve got you covered with our video editing glossary, which covers everyday terms like ‘cut’ and ‘transition’ to more complicated stuff like ‘key-frame’ or ‘chroma key’.
To make it even easier for you to save and reference back, we’ve created our video editing terms in alphabetical order.
Where there’s more to be said than just a simple definition, we’ll link you to some of our more in-depth articles and tutorials so you can learn more!
Video Editing Glossary: Jump to content in this section
Film Editing Terms: A - C



1. A-Roll
A-Roll is the footage that becomes the main part of your film, things like interviews, dialogue, or scenes that move the narrative on.
2. Aspect Ratio
Aspect ratio is the relationship between the width and height of your video frame (or an image). Common aspect ratios include 16:9 (widescreen and the most widely used one in film) and 4:3 (standard). If you take 16:9 as an example, then for every 16 pixels in width there are 9 in height.
3. Audio Level
Audio level is the volume of audio in a video. It’s measured in decibels (dB) and can be adjusted for clear and balanced sound, though experts agree that this should never be above 0dB to avoid distortion.



4. Bitrate
Bitrate is the amount of data transmitted or processed in a particular amount of time. It’s usually measured in bits per second (bps).
5. B-roll
B-roll is the supplemental footage that’s used to enhance the narrative or to give some context. You might see it during interviews or voiceovers, when we see something else instead of the person talking.
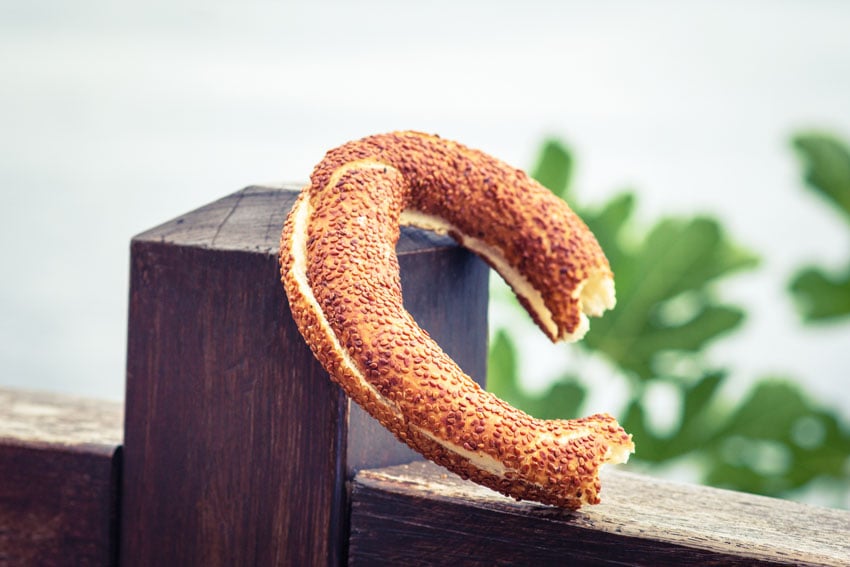
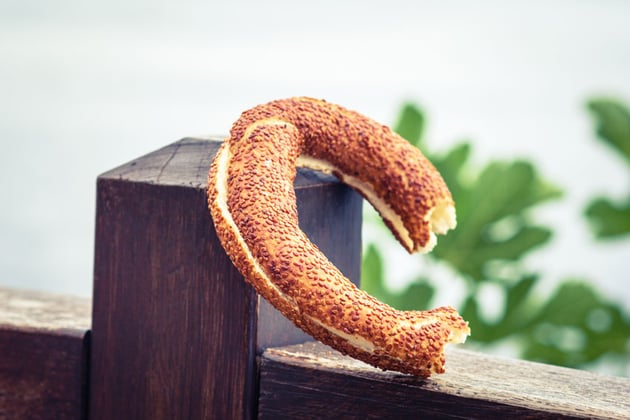



6. Chroma Key
Chroma key is a visual effects technique where a colour (usually green or blue) is replaced with another image or video. These colours are used because they’re not generally found elsewhere in the shot so they’re easy to ‘key out’ (remove).
7. Clip
A clip is a single piece of video or film footage, and that could be anything from a few seconds to several minutes in length.
8. Codec
A codec (coder-decoder) is used to compress digital files for storage and then to ‘unpack’ those at the other end where they’re viewed. Codecs can be hardware or software and popular ones used are H.264 (or H.265) and VP9. See also: Compression.
9. Colour Correction and Grading
Colour correction is the process of adjusting and enhancing the colour and contrast of video footage to get it to a neutral state (from a flat log file back to looking ‘normal’ for example), and then colour grading is adjusting it again but in order to create a particular look or style.
10. Compression
Compression is all about reducing the file size of a video by scrapping non-essential data, while maintaining a balance with quality. This needed for a variety of reasons but in particular with videos to be streamed over the internet. See also: Codec.
11. Container (or Wrapper)
A file format that stores your data, including the audio, video, and metadata. Containers are different from codecs, as each container format supports different codecs and features. Popular containers are MP4, AVI, MOV and so on.
12. Continuity
Continuity is basically keeping some consistency in your visual elements, like props and costumes, or actor positions, across different shots or scenes.
13. Cross-Fade
A cross fade is a transition with one shot gradually fading out and another simultaneously fading in, so it’s smooth and seamless. We won’t go into all the transitions, but this is one of the most used types.
14. Cut
A cut is the most basic editing technique, where one shot is replaced by another.
15. Cutaway
A cutaway is a shot that interrupts the main action to show something related that gives the audience context or helps with storytelling but doesn’t actually move the narrative along.
Advanced Editing in Adobe Premiere Pro: A Premiere Pro Workflow
Once you’ve got the basics, check out our advanced course! Advanced Premiere Pro for Everyone | FREE COURSE
Film Editing Terms: D - K
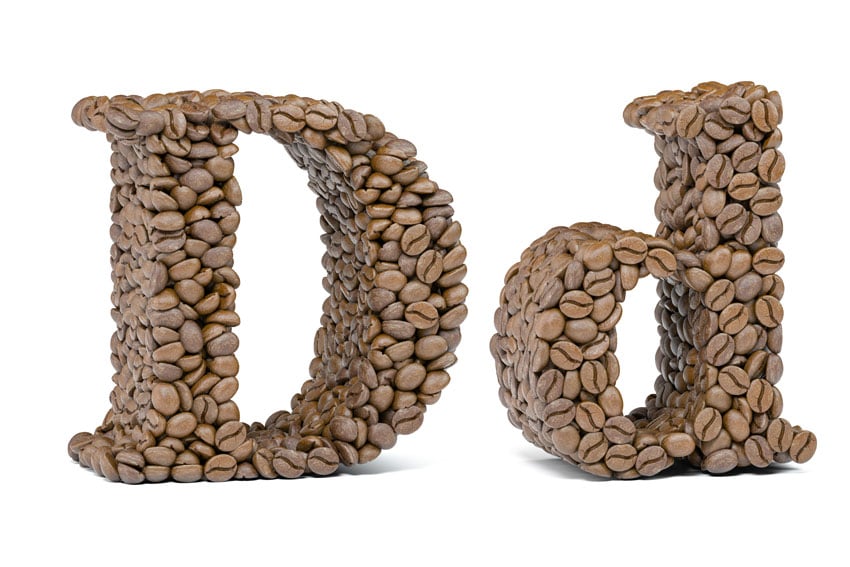
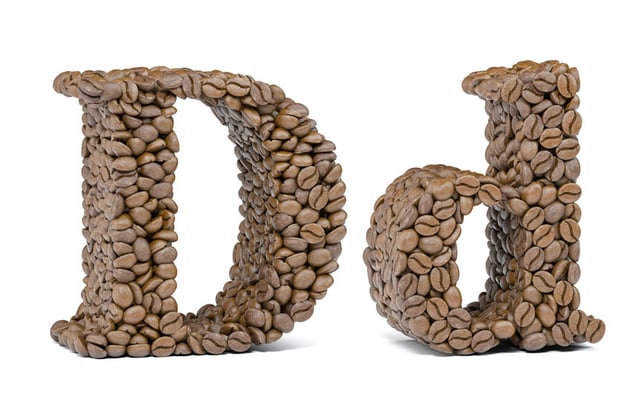
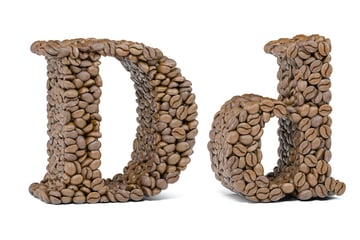
16. Dailies (also: Rushes)
Dailies, Rushes, or sometimes Daily Rushes are unedited pieces of footage shot each day during production. These are reviewed by the director or other crew members.



17. Export
Exporting is the process of saving your finished film or sequence to a video file format so it can be viewed on the intended device or platform.



18. Foley
Recording (or recreating) and adding sound effects and everyday sounds to a film during post-production.
19. Frame Rate or FPS
The number of individual frames or images displayed per second in a video. Common frame rates are 24fps (film standard), 30fps (television standard), and 60fps (high frame rate).
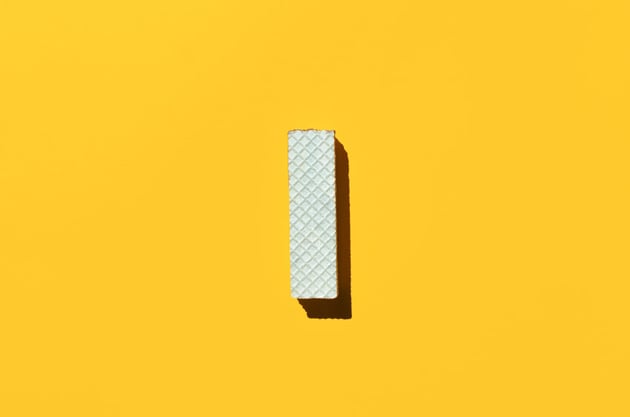



20. Importing
How media files and assets are transferred into the video editing software. This might involve converting files into a compatible format.
21. In Point
An in point is the start of a piece of video or audio, to show where playback or editing should start.



23. J-cut (and an L-Cut)
A J-cut is where the audio from the next shot starts before we see the visuals – this is the opposite of an L-cut where the audio continues into the next shot.
24. Jump Cut
An abrupt transition between two shots.
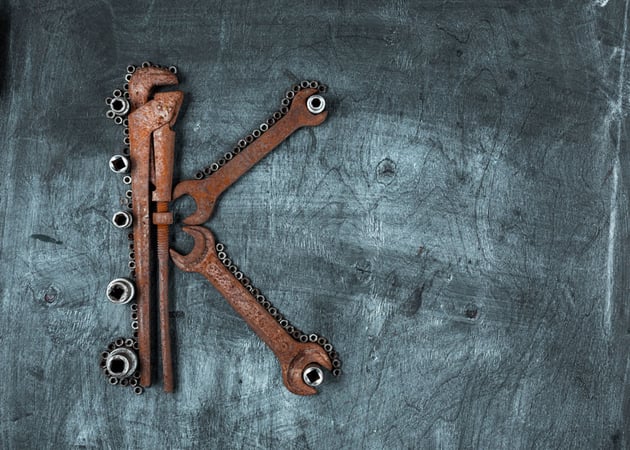



25. Keyframe
A keyframe is a specific frame in the video timeline where you make a particular change. They’re used to create animations and motion effects.
DaVinci Resolve 18 Tutorial | Beginners’ Quick-Start Guide
Need to get started with DaVinci Resolve but don’t know where to dive in? No stress; everyone has to start somewhere. That’s why Tom created the quick start guide for beginners!
Video Editing Terms: L - R
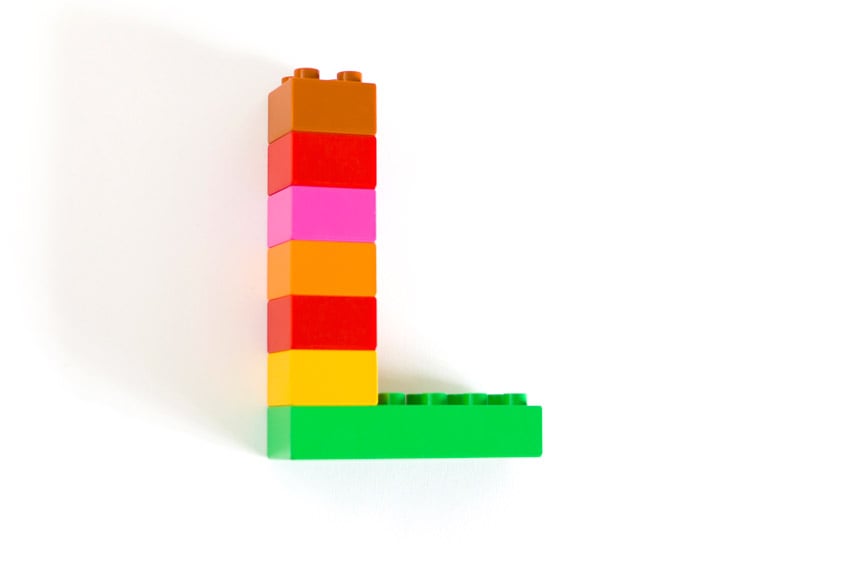
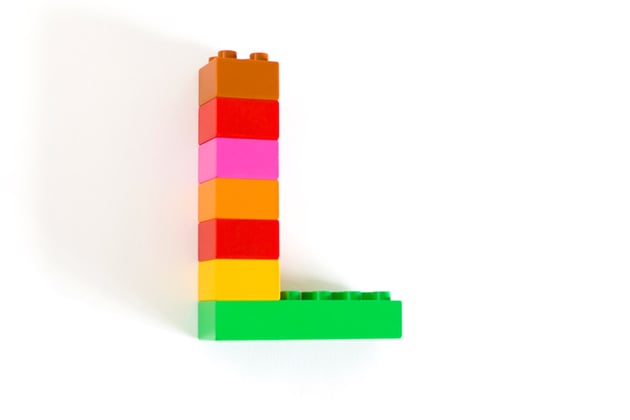
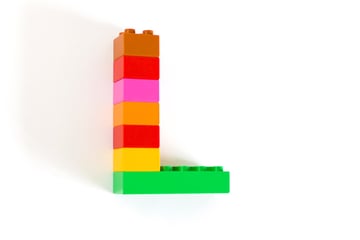
26. Lower Third
A lower third is a graphic overlay usually placed in the lower third (we see how it got its name) of the screen. They display contextual information like an interviewee’s name and title, a location, etc.
27. Luma
The brightness or luminance of an image – the intensity of the light in each pixel. Luma determines the overall brightness and contrast of your clip.
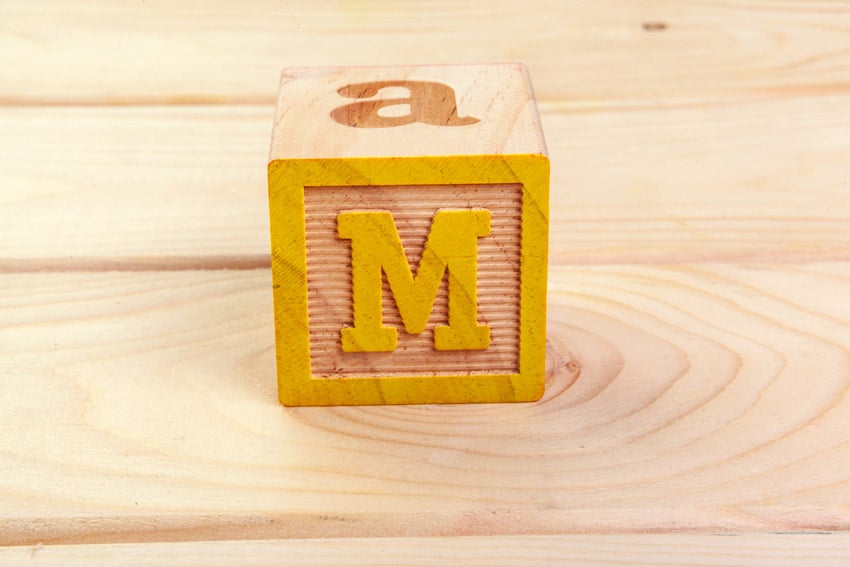
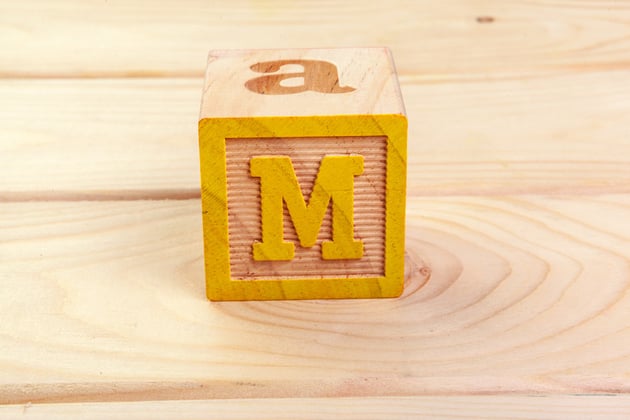



28. Masking
Selectively hiding or revealing parts of our footage using shapes or paths, like when compositing or creating visual effects.
29. Montage
A sequence of rapidly edited shots that express the passage of time, emotions, or ideas. It’s often used to condense information or character development.
30. Motion Graphics (or VFX)
Digital animations or visual effects that could include 3D animation, motion tracking, and other combinations of text, graphics, and movement.
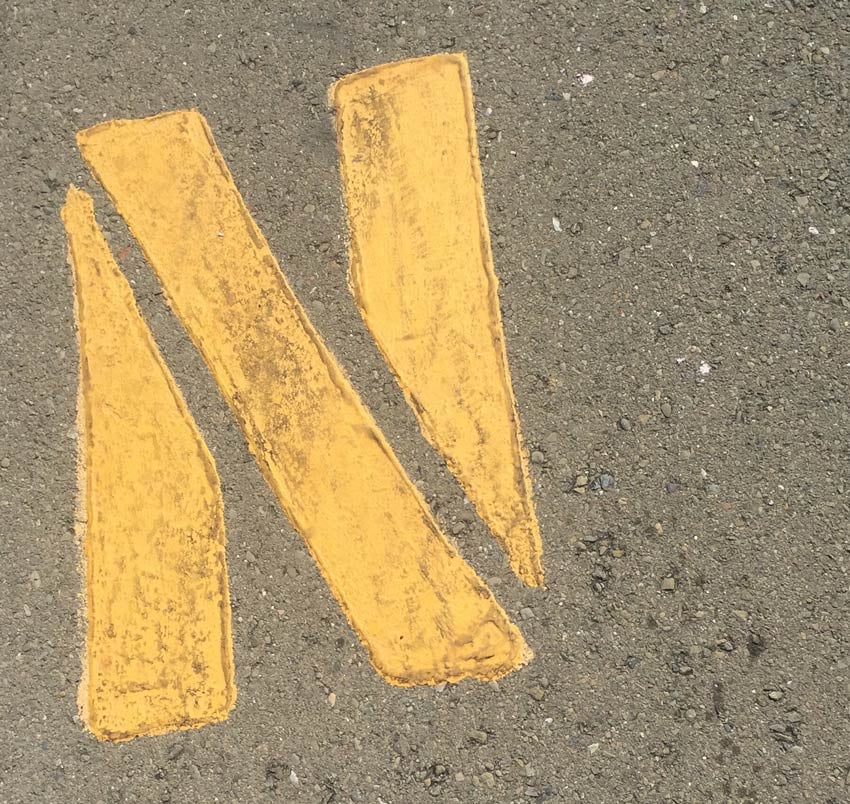
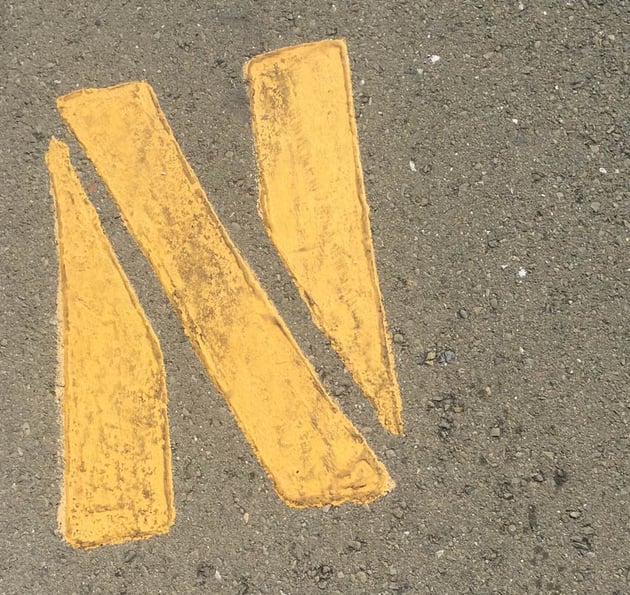



31. NLE (Non-Linear Editing)
Prior to digital there was only linear editing, but in digital video editing you can work out of order, arranging and modifying your files in whichever order you like!
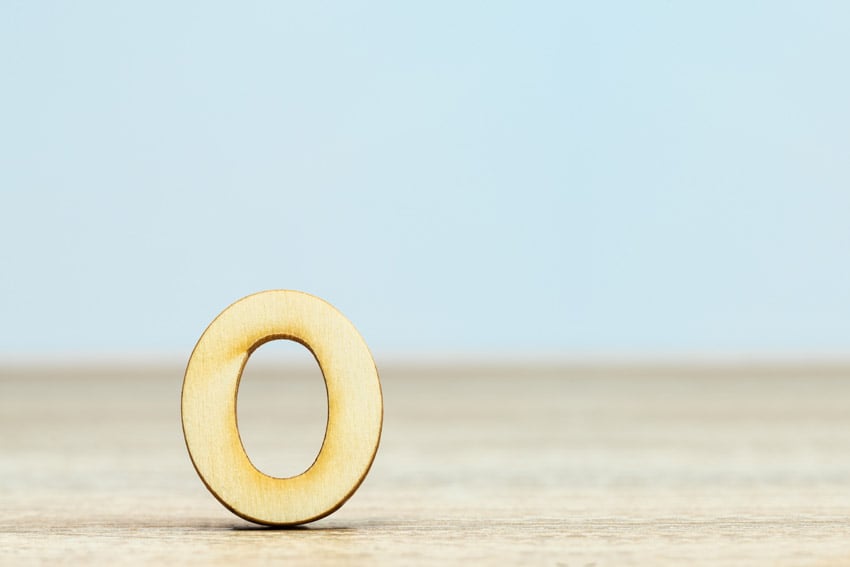
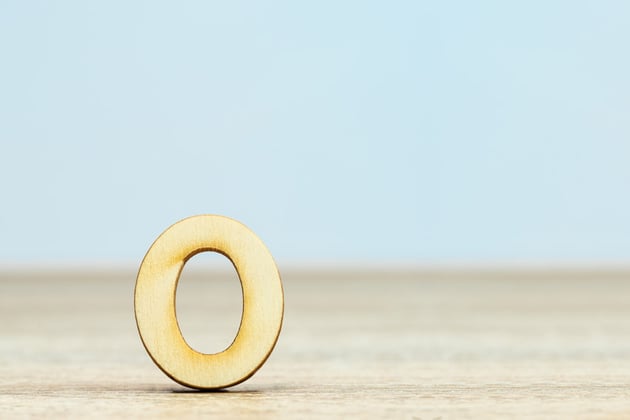



32. Out Point
An out point is the end of a selected part of video or audio, where playback or editing should end in a clip.
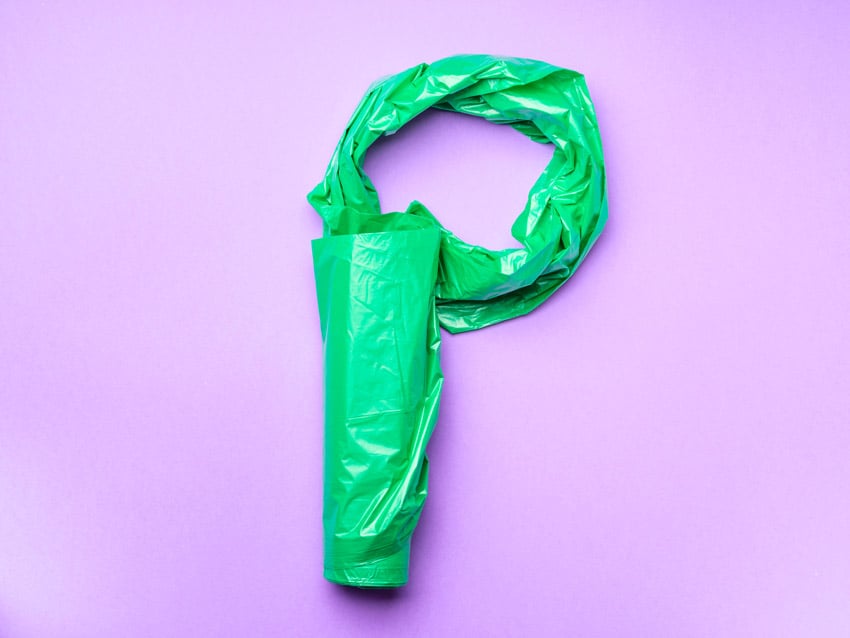
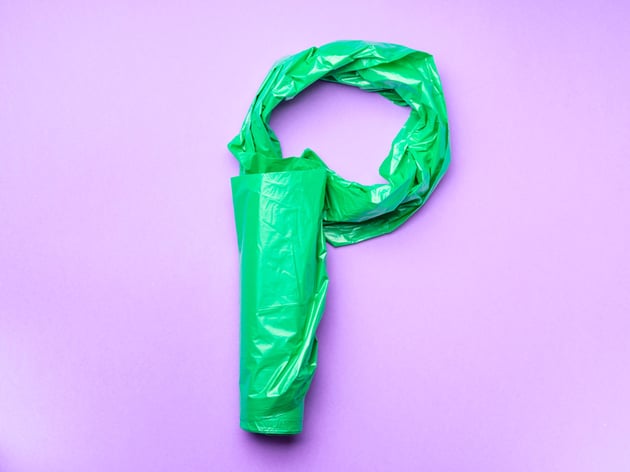



33. Playback
Viewing or listening to content with the aim of reviewing and adjusting the work.
34. Project File
A digital file that has all the data, assets, settings, and edits for a video editing project. It’s used to save and reopen projects for further editing or exporting. Project files are usually proprietary, so they only work properly in the software they’re created in.
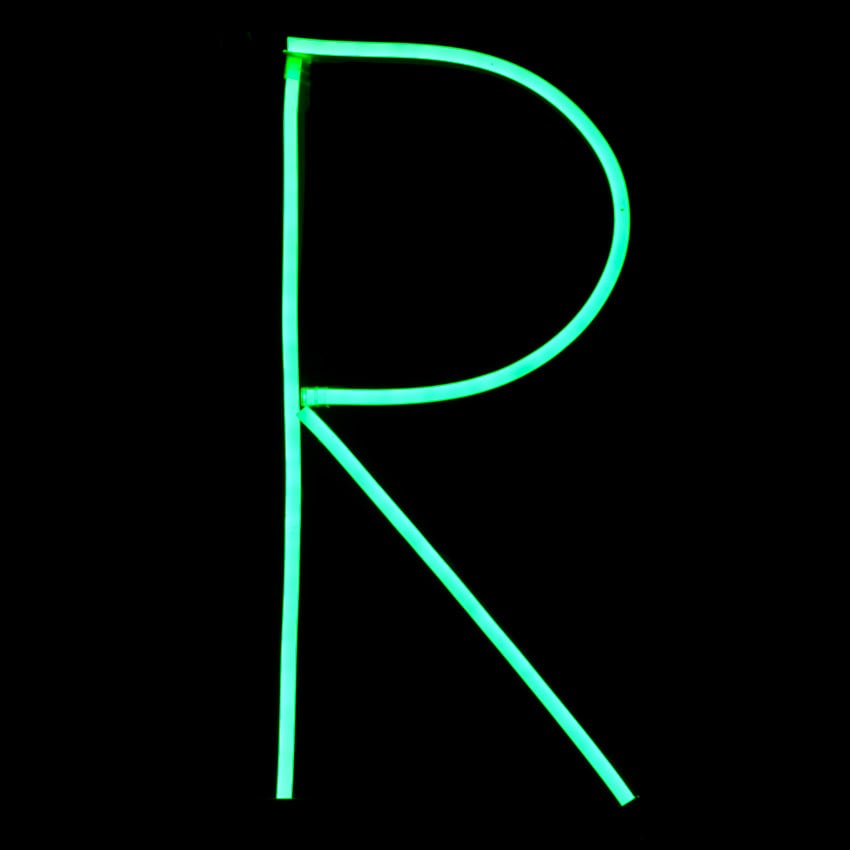
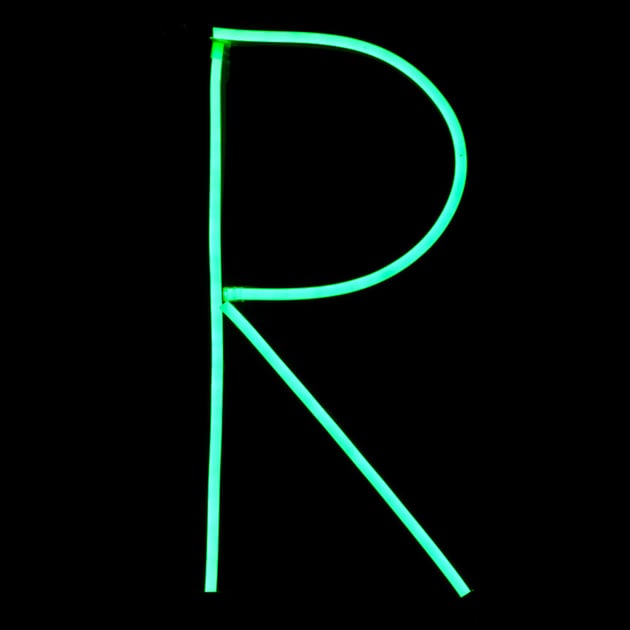

35. Render
Rendering is ‘flattening’ your video project into one file suitable to send on.
36. Resolution
Resolution is the clarity and detail of the video, usually measured in pixels. These include HD (1920x1080 pixels) and 4K (3840x2160 pixels).
How to Edit Audio in Premiere Pro | FREE COURSE (Over 5 Hours!)
Learn audio processing for video in Adobe Premiere Pro. In this 5+ hour free course, you will learn how to edit, process, mix, and master audio for your video projects. By the end of this course, you will have the skills you need to be able to tackle the audio portion of your projects like a pro!
Video Editing Terms: S - W



37. Scrubbing
Scrubbing manually through your footage by dragging the cursor or playback indicator along the timeline.
38. Selects
Remember Dailies/Rushes? Well, this is similar but rather than all of the footage it refers to the bits chosen (or selected…) to potentially be used in the final project.
39. Slip
Adjusting the timing of a clip within the timeline without changing the duration or position relative to other clips.
40. Slug
A placeholder or filler clip used to represent something that hasn’t been done yet, but so that you can plan around it and keep some rough pacing.
41. Sound Design
Creating and manipulating audio elements, which could include speech, music, and sound effects, to enhance the overall experience of a film.
42. Speed Ramp
The playback speed of a clip is gradually increased or decreased within the same shot.
43. Split Screen
Multiple shots or images are displayed simultaneously within the same frame, maybe to compare two (or more) actions or events, to show different perspectives, or to see two simultaneous events.
44. Storyboard
A storyboard is a visual representation of a video or film project, usually with a series of illustrations or images that outline the sequence of shots and scenes. These can be very rough outlines.
45. Syncing
Syncing is how you align audio and video tracks to make sure they play back properly – so when someone speaks, the visuals of them should match the audio perfectly.



46. Thumbnail
A thumbnail is a small, low-resolution image that represents a video, usually used as a preview or placeholder in software or on online platforms, like YouTube.
47. Titling
Titling is adding text or graphics to a video and includes titles, credits, subtitles… and so on.
48. Timeline
Your timeline is the workspace in your editing software where clips (and other assets) are arranged and edited.
49. Transition
A transition is a visual effect used to move from one shot to another. Common types include cuts, fades, dissolves, and wipes.



50. Watermark
A watermark is a usually translucent logo, text, or graphic overlayed on top of video footage to show who made it.
Motion Tracking in Premiere Pro | FAST!
Want to know how to motion track your footage in Premiere Pro? Join Tom for this Tuts+ Quick Tip as he shows you how to quickly and easily create motion trackers to add a little wow factor to your edits.
Conclusion
We hope you’ve found our video editing terminology guide for beginners useful. Why not bookmark it for future reference, and remember to check out some of the free video tutorials and courses we’ve mentioned through our guide.
Envato Elements
If you’re a video editor, then you’ll be able to make great use of Envato Elements, where you’ll discover thousands of video assets to use for one monthly subscription. These include video templates, overlays, backgrounds, music tracks, and so much more.
And if you love freebies then check out the monthly free files Elements has to offer, where you’re bound to find something that’s perfect for your next film project!
More Great Video Resources for Free


 10 Best Online Cloud Video Storage Solutions for 2024
10 Best Online Cloud Video Storage Solutions for 2024

 Marie Gardiner28 Feb 2024
Marie Gardiner28 Feb 2024

 10 Best Size Reducer Video Compression Software (Free & Paid 2024)
10 Best Size Reducer Video Compression Software (Free & Paid 2024)

 Jonathan Lam21 Feb 2024
Jonathan Lam21 Feb 2024

 10 Best Film Script Screenwriting Software (Free & Paid 2024)
10 Best Film Script Screenwriting Software (Free & Paid 2024)

 Marie Gardiner21 Feb 2024
Marie Gardiner21 Feb 2024

 What is Realism in Film, TV, and Video?
What is Realism in Film, TV, and Video?

 Marie Gardiner13 Feb 2024
Marie Gardiner13 Feb 2024
About This Page
This page was written by Marie Gardiner. Marie is a writer, author, and photographer. It was edited by Gonzalo Angulo. Gonzalo is an editor, writer and illustrator.
















